- The same kind of plants grown on a large scale at a place is called _________
- An important task in growing crops is _________ of soil.
- Damaged seeds would ___________ on top of the water.
- For growing crop sufficient sunlight and _________ and _________ from the soil are essential.
- crop
- preparation
- float
- water, nutrients
The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
2.Drip system. In this system, the waterfalls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. This system consists of the main pipe to which lateral pipes are joined. The specially prepared nozzles are attached to these lateral pipes. The nozzles are grounded just near the roots of the plants. It provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
Answer:
If wheat is sown in the Kharif season then it would not grow because a lot of water due to rain will spoil the seeds. Wheat crops require low temperature which it does not get in the Kharif season. Therefore, the quantity of wheat produced will be very less and quality will also be very poor.
- Mechanical method. Uprooting weeds with khurpi or hand, ploughing, burning, and flooding.
- Cultural method, lb prepare proper seedbed and sowing of seed timely and intercropping and crop rotation are the methods included under cultural method.
- Chemical method. By spraying chemicals known as herbicides or weedicides e.g. 2,4-D fluchloralin etc.
Question 10.Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production:
- The loosened soil allows the roots to penetrate freely, deeper, and breathe easily.
- The loosened soil also helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes, who are friends of the farmer, since they aid in further turning and loosening the soil and add humus to it.



Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Textbook Questions and Answers
(i) female Anopheles mosquito
(ii) cockroach
(iii) housefly
(iv) butterfly
Answer:
(i) Female Anopheles Mosquito
(i) nitrogen inflation
(ii) moulding
(iii) fermentation
(iv) infection
Answer:
(iii) fermentation
Question 7.Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
- Microorganisms are utilized in the preparation of wines, pickles, vinegar, cheese, curds, the aroma in tobacco.
- They are used in the production of antibiotics.
- They help in sewage disposal.
- Some soil bacteria like Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen, which is useful for plants.
- Some microorganisms are used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine, and acetic acid.
- Milk is turned into curd by bacteria.
- Some bacteria help in tanning leather.
- Some microorganisms are used to produce vaccines.
- They clean the environment.
- Some bacteria tenderize meat by breaking down muscle fibers.
- They cause a number of diseases in men, plants, and animals.
- Some microorganisms spoil milk, pickles, jams, squashes, and other food items.
- They damage the crops and thus, reducing productivity.
Answer:
Answer:
Rabies, polio, chickenpox, common cold, influenza (flu), and mosaic of tobacco and potato are the diseases caused by viruses.
- They bring about the decomposition of wastes in the soil and thus, increase the fertility of the soil.
- Some of the putrifying bacteria decompose the matter of sewage and help in sewage disposal.
- Some bacteria help in tanning leather.
- Bacteria tenderize meat by breaking down muscle fibers.
- Curd, cheese, etc. are formed by the action of bacteria in the milk.
- The fermentation activity of bacteria is useful in the preparation of vinegar, wine, palm juice, etc.
- Filamentous bacteria are used in the production of antibiotics.
- Some bacteria like Rhizobium can fix the nitrogen of the atmosphere, thus, enriching the soil in the nitrogen contents.
Answer:
Lactobacillus.
Question 11.
- Name the common antibiotic.
- Name the antibiotics made from bacteria and fungi.
Answer:
- Penicillin
- Streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin.
Question 13.Draw a diagram to show blue-green algae.
Answer:
Question 14.Describe the role of blue-green algae in the fertility of the soil.
Answer:
Blue-green algae have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds. It increases the humus content of the soil. This improves the water-holding capacity of the soil. Due to these reasons, the fertility of the soil is increased and hence, crop growth is also increased.
Question 15.What are pathogens?
Answer:
Microorganisms causing diseases in human beings, plants, and animals are called pathogens.
Question 16.How do disease-causing microorganisms enter our bodies?
Answer:
Disease-causing microorganisms enter our body through the air we breathe, the water we drink, or the food we eat; or transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or through an animal carrier.
Question 17.What are communicable diseases?
Answer:
Communicable diseases are those microbial diseases which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, food, or physical contact e.g., malaria, T.B, AIDS, cholera, common cold, chickenpox, etc.Question 18.How is the plasmodium parasite causing malaria transmission?
Answer:
Plasmodium parasite is transmitted by the bite of the female anopheles mosquito. Anopheles mosquito merely acts as a carrier of malaria-causing parasites. It takes them alongwith the blood sucked from an infected person and transmits them to a healthy person.

Answer:
Disease – Causative microorganism
Chicken Pox – Virus
Polio – Virus
Answer:
Chicken Pox – Air, contact
Polio – Air, water.
Answer:
Bacteria.
Answer:
Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium.
Answer:
Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
Answer:
Bacillus anthracis.
Answer:
Robert Koch (1876).
Answer:
Citrus canker. Its mode of transmission is air.
Answer:
Rust of wheat. Its mode of transmission is insects and seeds.
Answer:
Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi. Its mode of transmission is insect.
Answer:
Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances. These make the food poisonous causing serious illness and even death.
Answer:
Food poisoning is due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
Question 31.Is spoiling food a chemical reaction?
Answer:
Yes.
Answer:
Spoiled food emits a bad smell and has a bad taste and changed colour.
Answer:
The role of nodules in the biological fixation of nitrogen is to fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates.
Answer:
Rhizobium, Clostridium, and Azotobacter.
Answer:
Nitrogen. Our atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen gas.
Question 36.In which form is nitrogen present in all living organisms?
Answer:
Proteins, chlorophyll, nucleic acids, and vitamins.
Answer:
The various stages of the nitrogen cycle are:
In the soil nitrogen is present in the form of nitrates by the following processes:
Nitrogen and oxygen combine to form nitric acid at the time of lightning in the atmosphere. This nitric acid forms nitrates which reach the earth with rainwater.
Nitrates are formed in the soil from the decay of dead plants and animals.
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria present in soil and root nodules of some leguminous plants convert the nitrogen in the air directly into nitrates.
The plants absorb nitrates from the soil and convert them into plant proteins and plant protoplasm.
The animals eat plants and convert plant proteins into animal proteins.
The plant proteins and animal proteins of dead plants and animals are converted into ammonia in the soil by bacterial decomposition.
Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and these nitrates are converted into nitrates in the soil.
Some of the nitrates formed in the soil are converted back into free nitrogen gas by
denitrifying bacteria. This free nitrogen gas goes back into the atmosphere and the nitrogen cycle is repeated again and again.
Collect some moist soil from the field in a beaker and add water to it. After the soil particles have settled down, observe a drop of water from the beaker under a microscope.
Question (i).What do you sec?
Answer:
We see tiny organisms under a microscope.
Activity 2
Take a few drops of water from a pond. Spread on a glass slide and observe through a microscope.
Question (i).Do you find tiny organisms moving around?
Answer:
Yes.
Take 1/2 kg flour (atta or mauia), add some sugar, and mix with warm water. Add a small amount of yeast powder and knead to make a soft dough.
Question (i).What do you observe after two hours? Did you find the dough rising?
Answer:
After two hours we find the dough rising.
Activity 4
Take a 500 mL beaker filled upto 3/4 with water. Dissolve 2-3 teaspoons of sugar in it. Add half a spoon of yeast powder to the sugar solution. Keep it covered in a warm place for 4-5 hours. Now smell the solution.
Question (i).Could you get a smell?
Answer:
Yes, I can smell alcohol.
Take two pots and fill each pot half with soil. Mark them A and B. Put plant waste in pot A and things like polythene bags, empty glass bottles, and broken plastic toys in pot B. Put the pots aside. Observe them after 3-4 weeks.
Question (i)Do you find any difference in the contents of the two pots?
Answer:
Yes.
Answer:
Plant waste in pot A gets decomposed whereas there is no change in contents of pot B.
Answer:
The plant waste gets converted into manure by the action of microbes.
Question (iv).Why do the contents of pot B (polythene bags, empty glasses, bottles, and broken toys) did not undergo any change?
Contents of pot B (polythene bags, empty glasses, bottles, and broken toys) did not undergo any change because microbes could not ‘act’ on them and convert them into manure.
Answer:
Some fibers are called synthetic because they are made by human beings, e.g., polyester, acrylic etc.
Rayon is different from synthetic fibers because:
(i) It has a silk-like appearance.
(ii) It is obtained from wood pulp.
(iii) Its fibres can also be woven like those of natural fibres.
Answer:
(ii) It is obtained from wood pulp.
Question 3.Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
Synthetic fibres are also called _____ or _____ fibres.
Synthetic fibres are synthesised from raw material called _____
Like synthetic fibres, plastic is also a _____
Answer:
artificial or man-made
petrochemicals
polymer.
Answer:
Parachutes and ropes for rock climbing.
Answer:
The three main advantages of using plastic containers for storing food are:
Plastic is nonreactive.
Plastic is light, strong, and durable.
Plastic is cheap.
Question 6.Explain the difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics.
Answer:
The difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting plastics is:
Thermoplastics soften on heating and then can be moulded into various shapes. They can be melted and shaped any number of times, e.g. polythene, PVC. BUT
Thermosets are plastics which once set, do not soften on heating. They retain the shape in which they were originally moulded. They are harder and stiffer than thermoplastics, e.g. bakelite, melamine.
Saucepan handles.
Electric plugs/switches/plugboards.
Answer:
Saucepan handles are made of thermosetting plastics (bakelite) because it is a poor conductor of heat.
Electric plugs/switches/plug boards are made of thermosetting plastics (bakelite) because it is a poor conductor of electricity.
Telephone instruments, toys, cooker handles, carry bags, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls, electric wire covering, plastic chairs, electrical switches.
Answer:
Can be recycled: Telephone instruments, plastic toys, ballpoint pens, plastic bowls.
(As these are thermoplastics, so these can be recycled).
Cannot be recycled: Cooker handles, carry bags, plastic covering on an electric wire, plastic chairs, etc.
(As these are thermosetting plastics, these cannot be recycled).
Answer:
We would advise Rana to buy cotton shirts because cotton clothes absorb sweat in summers whereas synthetic fibers do not absorb sweat and stick to the body making one feel uncomfortable.
Question 10.Give examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature.
Answer:
Examples to show that plastics are non-corrosive in nature:
A wide range of chemicals is stored in plastic containers.
Food items are stored in plastic containers.
(Different buckets and mugs are made of plastics.
Answer:
No, the handle and bristles of a toothbrush should not be made of the same materials because the handle of the toothbrush must be hard and thus is made of thermosetting plastic whereas bristles of a toothbrush are made up of nylon which is soft, flexible, and strong.
Answer:
Plastic takes several years to decompose. It is not environment friendly. It causes environmental pollution. Besides, the burning process in the synthetic material is quite slow and it does not get completely burnt easily. In the process, it releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution. Therefore, avoid the use of plastics as far as possible. The plastics garbage should be recycled.
Match the terms of column A correctly with the phrases given in column B.
Column A Column B
(i) Polyester (a) Prepared by using wood pulp
(ii) Teflon (b) Used for making parachutes and stockings.
(iii) Rayon (c) Used to make non-stick cookware.
(iv) Nylon (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily.
Column A Column B
(i) Polyester (d) Fabrics do not wrinkle easily.
(ii) Teflon (c) Used for making non-stick cookware.
(iii) Rayon (a) Prepared by using wood pulp.
(iv) Nylon (b) Used for making parachutes and stockings.
Answer:
Synthetic fibers are obtained by chemical processing of petrochemicals and not from fibres obtained from plant and animal sources. Hence we do not have to cut trees for manufacturing synthetic fibres and thus forests are conserved.
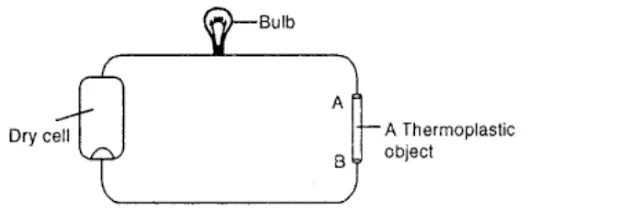
Question 15.Describe an activity to show that thermoplastic is a poor conductor of electricity.
Answer:
Take a dry cell to connect conducting wires and electric bulb with it, keeping a gap of 5 cm between two ends (A and B) of conducting wares in the circuit. Place an object of thermoplastic in the gap making sure that it touches the ends of the wires and thus the circuit is completed.
Answer:
Fabrics are made using fibres obtained from natural or artificial sources.
Question 2.Name few natural fibers.
Answer:
Jute, cotton, silk, and wool.
Question 3.Name few artificial fibers.
Answer:
Rayon, terylene, nylon, polythene, Teflon, etc.
Question 4.What is a polymer?
Answer:
Polymer (poly means many, mers means parts) is a large molecule comprised of repeating structural units (monomers) joined together. There may be hundreds or even thousands of structural units in a polymer.
Question 5.What is rayon?
Answer:
The artificial silk prepared from cellulose is called rayon.
Question 6.Write the uses of rayon?
Answer:
The uses of rayon are:
Rayon mixed with cotton is used for making nurses’ dresses. Rayon makes them easier to wash and more hygienic.
Rayon mixed with wool is used for making carpets. Rayon makes them lighter and more durable.
Rayon gauze is used in bandaging. Rayon gauze can absorb over 90% of its own weight of water. Rayon gauze does not adhere to wounds.
Question 7.How is nylon prepared?
Answer:
Nylon is prepared from coal, water, and air.
Question 8.Write the properties of nylon.
Answer:
The properties of nylon are:
It is strong, elastic, and light.
It is lustrous and easy to wash.
Question 9.Why is polyester suitable for making dress material?
Answer:
Polyester is suitable for making dress material because this fabric does not get wrinkled easily. It remains crisp and easy to wash.
Question 10.What is PET? What are its uses?
Answer:
PET is a very familiar form of polyester. PET is used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires, and many other useful products.
Question 11.Why we should never wear polyester clothes while working in the kitchen or in a laboratory?
Answer:
We should never wear polyester clothes while working in the kitchen or in a laboratory because in case of fire the polyester fabric melts and sticks to the body of the person wearing it.
Question 12.How are all synthetic fibres prepared?
Answer:
All synthetic fibres are prepared by a number of processes using raw materials of petroleum origin called petrochemicals.
Question 13.Write unique characteristics of synthetic fibers} which make them popular dress materials.
Answer:
The unique characteristics of synthetics fibers are:
They dry up soon
Are durable
Less expensive
Readily available
Easy to maintain
Question 14.What are plastics?
Answer:
Plastics are polymers of very high molecular masses. They are generally not affected by acids or alkalis. They can be moulded to any desired shape.
Question 15.Why storing any food item, water, milk, pickles, dry food, etc. Plastic containers seem most convenient?
Answer:
Storing any food item, water, milk, pickles, dry food, etc. plastic containers seem most convenient because of their lightweight, lower price, good strength, and easy handling.
Question 16.Which property of plastic makes it useful in cars, aircraft, and spacecraft?
Answer:
Plastics are lighter compared to metals, therefore, they are useful in cars, aircraft, and spacecraft.
Question 17.Which material is called biodegradable?
Answer:
A material which gets decomposed through natural processes, such as action by bacteria, is called biodegradable.
Question 18.Which material is called non-biodegradable?
Answer:
A material which is not easily decomposed by natural processes is termed non-biodegradable.
Question 19.The disposal of plastic is a major problem. Why?
Answer:
Disposal of plastic is a major problem because:
It takes several years to decompose.
If burnt that it takes a long time to get completely burnt and in the process, it releases a lot of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
Activities
Activity 1
Make a list of some common articles made from fibers. Try to separate them into those made from natural fibers and those made from artificial fibers. Make entries in Table (a).
Table (a): Natural and Artificial Fibres
Name of Article Type of Fibre (Natural/artificial)
1. Acrylic sweater Artificial
2. Woollen sweater Natural
3. Cotton shirt Natural
4. Nylon saree Artificial
5. Nylon tents Artificial
Question (i).Why did you label some fibers as artificial?
Answer:
We have labelled some fibres as artificial because they are man-made fabrics.
Activity 2
Take an iron stand with a clamp. Take a cotton thread of about 60 cm in length. Tie it to the clamp so that it hangs freely from it as shown in Fig. 1. At the free end suspend a pan so that weight can be placed in it. Add weight one by one till the thread breaks. Note down the total weight required to break the thread. This weight indicates the strength of the fiber. Repeat the same activity with threads of wool, polyester, silk, and nylon. Tabulate the data as shown in Table. Arrange the threads in order of their increasing strength.
Question 1.Which of
the following can be beaten into thin sheets:
(a) Zinc
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Sulphur
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(a) Zinc
Question 2.Which of
the following statement is correct?
(a) All metals are ductile.
(b) All non-metals are ductile.
(c) Generally, metals are ductile.
(d) Some non-metals are ductile.
Answer:
(d) Generally, metals are ductile.
Question 3.Fill in the blanks:
1. 1 Phosphorus is a very _______ non-metal.
2.Metals are _______ conductors of heat and __________
3.Iron is _______ reactive than copper.
4.Metals react with acid to produce __________ gas.
Answer:
1. reactive
2. good,
electricity
3. more
4.
hydrogen
Question 4.Mark ‘T’ if
the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
1.
Generally, non-metals react with acids.
2.
Sodium is a very reactive metal.
3.
Copper displaces zinc from zinc sulphate solution.
4.
Carbon can be drawn into wires.
Answer:
1.
False
2.
True
3.
False
4.
False
Question 5.Some
properties are listed in the following table. Distinguish between metals and
non-metals on the basis of these properties:
|
Properties |
Metals |
Non-metals |
|
1. Appearance |
||
|
2. Hardness |
||
|
3. Malleability |
||
|
4. Ductility |
||
|
5. Heat conduction |
||
|
6. Conduction of electricity |
Answer:
|
Properties |
Metals |
Non-metals |
|
1. Appearance |
Lustrous (shiny) |
Non-lustrous (dull) |
|
2. Hardness |
Very hard |
Soft |
|
3. Malleability |
Malleable |
Not malleable |
|
4. Ductility |
Ductile |
Not ductile |
|
5. Heat conduction |
Good conductors |
Bad conductors of heat |
|
6. Conduction of electricity |
Good conductor of electricity |
Bad conductors of electricity |
Question 6.Give reasons for the following:
1.
Aluminium foils are used to wrap food items.
2.
Immersion rods for heating liquids are made up of metallic
substances.
3.
Copper cannot displace zinc from its salt solution.
4.
Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene.
Answer:
1.
Aluminium is non-toxic and malleable and hence thin sheets of
aluminium can be formed.
2.
Metallic substances are good conductors of electricity therefore
immersion rods are made up of metallic substances.
3.
Copper is less reactive than zinc and hence it cannot displace
zinc from its salt solution.
4.
Sodium and potassium are stored in kerosene because it
vigorously reacts with oxygen and water.
Question 7.Can you
store the lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil? Explain.
Answer:
No, we can not store the lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil because aluminium
is metal and thus will react with lemon and produce toxic substances.
Question 8.
Match the substance given in Column A with uses given in Column B.
|
A |
B |
|
(i) Gold |
(a) Thermometers |
|
(ii) Iron |
(b) Electric wire |
|
(iii) Aluminium |
(c) Wrapping food |
|
(iv) Carbon |
(d) Jewellery |
|
(v) Copper |
(e) Machinery |
|
(vi) Mercury |
(f) Fuel |
Answer:
|
A |
B |
|
(i) Gold |
(d) Jewellery |
|
(ii) Iron |
(e) Machinery |
|
(iii) Aluminium |
(c) Wrapping food |
|
(iv) Carbon |
(f) Fuel |
|
(v) Copper |
(b) Electric wire |
|
(vi) Mercury |
(a) Thermometers |
Question 9.What happens when:
(i) Dilute sulphuric acid is poured on a copper plate.
(ii) Iron nails are placed in a copper sulphate solution. Write word equations
of the reactions involved.
Answer:
(i) Copper reacts with sulphuric acid and forms copper sulphate and hydrogen
(gas).
Copper + Sulphuric acid → Copper sulphate + Hydrogen gas.
Cu + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2 ↑
(ii) Iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution hence a
reddish-brown copper is formed on the iron nails and the blue colour of copper
sulphate solution slowly becomes light green.
Iron + Copper sulphate → Copper + Iron sulphate.
Fe + CuSO4 → Cu + FeSO4
Question 10. Saloni took a piece of burning charcoal and
collected the gas evolved in a test tube:
(i) How will she find the nature of the gas?
(ii) Write down word equations of all the reactions taking place in this process.
Answer:
(i) To find the nature of the gas, she will dissolve it in the water and test
it with litmus paper.
(ii) (a) Charcoal (c) + Oxygen (O2) → Carbon dioxide (CO2)
(b) Carbon dioxide (CO2) + Water (H2O) → Carbonic acid (H2CO3)
The nature of this gas is acidic because it turns red litmus blue.
Question 11.One day
Reeta went to a jeweler’s shop with her mother. Her mother gave old gold
jewellery to the goldsmith to polish. The next day when they brought the
jewellery back they found that there was a loss in its weight. Can you suggest
a reason for the loss of weight?
Answer:
The jeweller must have cleared the jewellery in aqua regia solution. This
solution is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric
acid in the ratio of 3 : 1. This acid solution dissolves some gold in it, due
to which there is a loss in the weight of jewellery.
Question 1.Give examples of metals.
Answer:
Examples of metals are gold, silver, sodium tungsten, cadmium, nickel, uranium,
and mercury.
Question 2.Give
examples of non-metals?
Answer:
Examples of non-metals are chlorine, helium, oxygen, carbon, fluorine, sulphur,
iodine, and bromine.
Question 3.Name the
metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Answer:
Mercury
Question 4.Write
the physical properties of metals.
Answer:
The physical properties of metals are:
·
Metals are solid at room temperature except for mercury.
·
Metals generally have high melting points.
·
The surface of most metals has a shiny appearance.
·
Metals are malleable, i.e., they can be beaten into sheets.
·
Metals are ductile, i.e., they can be stretched into wires.
·
Metals are good conductors of electricity.
·
Metals are good conductors of heat.
·
Metals are sonorous, i.e., they produce sound when they are
struck by themselves or by any other object.
Question 5.
(i) What do you observe when magnesium ribbon is heated over a flame?
(ii) What change do you observe in the colour of red and blue litmus papers
when they are dipped into solution obtained by mixing solid residue from (i) in
water? What do you conclude?
(iii) Write chemical equations for the above two reactions.
Answer:
(i) When magnesium ribbon is heated over the flame then it burns with brilliant
light and gets converted into a white solid residue.
(ii) The solution
obtained by mixing white solid residue produced above with water turns red
litmus into blue colour and blue litmus remains unaffected. This shows that the
solution is alkaline hence oxide formed is basic in nature.
(iii) 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
Question 6.What happens when a small piece of sodium metal is
dried and kept in water?
Answer:
When a small piece of sodium metal is dried and kept in the water we observe
that the sodium piece starts moving in water with a hissing sound and sodium
catches fire.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2 ↑
Question 7.Does magnesium react with cold water? What happens
when the water is heated?
Answer:
Magnesium does not react or mildly react with cold water. When water is heated
then magnesium reacts with hot water or steam vigorously and produces magnesium
hydroxide and hydrogen.
Mg + 2H2O → Mg(OH)2 + H2
(Magnesium) + Water → Magnesium Hydroxide + Hydrogen
Question 8.How do
metals react with dilute acids?
Answer:
Metals usually displace hydrogen from dilute acids and salt is formed. Only the
less reactive metals like copper, silver, and gold do not displace hydrogen
from dilute acids.
Metal + Hydrochloric acid → Metal chloride + Hydrogen (gas)
Metal + Sulphuric acid → Metal sulphate + Hydrogen (gas)
Question 9.Write the word equation for the reaction of magnesium
with dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Magnesium reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid to form magnesium chloride and
hydrogen gas is evolved.
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Question 10.What happens when iron nails are added to copper sulphate solution?
Answer:
When iron nails are added to copper sulphate solution the blue colour of copper
sulphate starts fading and iron sulphate is formed. Iron displaces copper from
copper sulphate and copper gets deposited on the iron nails.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Question 11.What happens when strips of magnesium are added to iron sulphate solution?
Answer:
When strips of magnesium are added to iron sulphate solution then magnesium
displaces iron from iron sulphate solution and forms magnesium sulphate. Iron
gets deposited on the magnesium strips.
Mg + FeSO4 → MgSO4 + Fe
Question 12.What would you observe when a strip of zinc is dipped in the solution of copper
sulphate?
Answer:
When a strip of zinc is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate solution then
zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. A red-brown coating of
copper forms on the strips of zinc.
Question 13.Write the uses of metals.
Answer:
The metals are used for:
·
making machines
·
making buildings
·
making automobiles, aeroplanes, trains, satellites, industrial
gadgets
·
making cooking utensils and water boilers
·
making electric gadgets
·
making electric cables
·
fine electric contacts in computers and solar cells
·
for making jewellery, mirrors
·
making foils for wrapping of food items, medicines, chocolates,
cigarettes, etc.
Question 14.Why is iron used for making machines, automobiles, and buildings?
Answer:
Iron is very strong, hard, and rigid therefore, it is used for making machines,
automobiles, and buildings.
Activities
Activity 1
Take a small iron nail, a coal piece, a piece of thick aluminium wire, and a
pencil lead. Beat the iron nail with a hammer (Fig.). Try to hit hard. Hit hard
the aluminium wire also. Then repeat the same kind of treatment on the coal
piece and pencil lead. Record your observations in the table.
Table: Malleability of
Materials
|
Object/Material |
Change in shape (Flattens/Breaks into pieces) |
|
Iron nail |
Flattens |
|
Coal piece |
Breaks into pieces |
|
Aluminium |
Wire Flattens |
|
Pencil lead |
Breaks into pieces |
Activity 2
Recall how to make an electric circuit to test whether electricity can pass
through an object or not (Fig.).
Now, repeat the activity with the materials mentioned in the table. Observe and
group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors.
Table: Electrical
Conductivity of Materials
|
Materials |
Good Conductor/Poor Conductor |
|
1. Iron rod/nail |
Good Conductor |
|
2. Sulphur |
Poor Conductor |
|
3. Coal piece |
Poor Conductor |
|
4. Copper wire |
Good Conductor |
Activity 3
Let us check the nature of rust formed as a result of the reaction between
iron, oxygen, and water. Collect a spoonful of rust and dissolve it in a very
little amount of water. You will find that the rust remains suspended in water.
Shake the suspension well. Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers
(Fig.).
What do you observe? Is the solution acidic or basic?
Answer:
We observe that red litmus turns blue. The solution is basic.
Activity 4
Take a small amount of powdered sulphur in a deflagrating spoon and heat it. If
the deflagrating spoon is not available, you may take a metallic cap of any bottle
and wrap a metallic wire around it and give it the shape shown in Fig. (a).
As soon as sulphur starts burning, introduce the spoon into a gas jar/glass
tumbler [Fig.(a)]. Cover the tumbler with a lid to ensure that the gas produced
does not escape. Remove the spoon after some time. Add a small quantity of
water into the tumbler and quickly replace the lid. Shake the tumbler well.
Check the solution with red and blue litmus papers [Fig. (b)].
Question (i) What do
you observe?
Answer:
We observe that blue litmus turns red. Therefore, this solution is acidic.
Activity 5
Take a 250 ml beaker/glass tumbler. Fill half of it with water. Now carefully
cut a small piece of sodium metal. Dry it using filter paper and wrap it in a
small piece of cotton. Put the sodium piece wrapped in cotton into the beaker.
Observe carefully. When the reaction stops touch the beaker. What do you feel?
Has the beaker become hot? Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers.
Is the solution acidic or basic?
Question (i).What do you feel? Has the beaker become hot?
Test the solution with red and blue litmus papers. Is the solution acidic or
basic?
Answer:
Yes. The beaker becomes very hot. The solution is basic because it turns red
litmus blue.
Activity 6
Take samples of metals and non-metals listed in the table in separate test
tubes and label them as A, B, C, D, E, and F. With the help of a dropper add 5
ml of dilute hydrochloric acid to each test tube one by one. Observe the
reactions carefully. If no reaction occurs in the cold solution, warm the test
tube gently. Bring a burning matchstick near the mouth of each test tube.
Repeat the same activity using dilute sulphuric acid instead of dilute
hydrochloric acid. Record your observation in the table.
Table 5: Reaction of
Metals and Non-metals with Acids
|
Test tube Label |
Metal/Non-metal |
Reaction with Dilute Hydrochloric Acid Room Warm Temperature |
Reaction with Dilute sulphuric Acid Room Warm Temperature |
|
A |
Magnesium (ribbon) |
Hydrogen gas is liberated |
|
|
B |
Aluminium (foil) |
Hydrogen gas is liberated |
|
|
C |
Iron (filings) |
Hydrogen gas is liberated |
|
|
D |
Copper (peeled flexible wire) |
No reaction takes place |
Hydrogen gas is liberated |
|
E |
Charcoal (powder) |
No reaction takes place |
No reaction takes place |
|
F |
Sulphur (powder) |
No reaction takes place |
No reaction takes place |
Activity 7
Prepare a fresh solution of sodium hydroxide in a test tube by dissolving 3-4
pellets of it in 5 ml of water. Drop a piece of aluminium foil into it. Bring a
burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube. Observe carefully.
Answer:
We observe that a gas is produced which burns with a pop sound. This gas is
hydrogen gas.
Activity 8
Take five 100 ml beakers and label them A, B, C, D, and E. Take about 50 ml of
water in each beaker. Dissolve in each beaker a teaspoonful of each substance
as indicated in Fig. (a).
Keep the beakers undisturbed for some time. Record your observations in your
notebook.
Beaker A: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Zinc granule (Zn)
Beaker B: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Beaker C: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker D: Iron sulphate (FeSO4) + Copper turnings (Cu)
Beaker E: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Fig. (a) and (b) Displacement reactions.
Question (i).
What changes do you observe in the various beakers?
Answer:
In beaker A, zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate (CuSO4). The blue colour of copper sulphate
disappears and a powdery red mass of copper is deposited at the bottom of the
beaker.
Copper sulphate + Zinc → Zinc sulphate + Copper
In beaker B, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The blue
colour of copper sulphate disappears and it becomes light green. A red coloured
powder of copper is deposited on the copper.
In beaker C, D, E, there is no change.
No comments:
Post a Comment